International Prices
GetCatalogPrices API
Note
This API endpoint is used to pull the prices for international markets. If the merchant wishes it to be fully automated for new products, we need to make sure that they also upload through SFTP, otherwise, some new products may not exist in the Global-e Database.
Request sent by the merchant:
A list of countries - two letters country codes (ISO2), for which international prices product feed is required.
A list of products for which international prices product feed is required, with the following details for each product:
ProductCode (SKU) - ProductCode (SKU) for the product.
OriginalCurrencyCode - Optional. Currency code for the received product. If left empty, then the default merchant currency will be assumed.
OriginalSalePrice per product - Price in original currency.
VATRate - Local VAT rate of the product in the merchant country.
ProductClassCode - Optional. Product class code used by the merchant to overwrite country coefficient rate.
IsPriceIncludeVAT- Optional. The default value is True. Indicates whether the price includes the merchant country's local VAT rate.
Response sent by Global‑e:
The Merchant receives back a list of SKUs and related prices in the countries that were sent in the request.
GetCatalogPrices Method
GetCatalogPrices (FullProductCatalogRequest request)
Receives a conversion request from a merchant and returns the requested list of country and currency prices for the .
International Price Calculation (Mobile Platforms)
GetMerchantPriceDetails Overview
This Global-e GetMerchantPriceDetails REST API enables merchants to obtain the parameters required to calculate product prices in a destination country currency.
This document provides details about the GetMerchantPriceDetails API, a flow and explanations on how to implement the logic, and a sample implementation in JavaScript.
This document is intended for the developer in charge of evaluating and integrating the solution with the merchant's ecommerce platform and assumes familiarity with the Global-e technology, concepts, and terminology.
Calculating Prices: Logic and Flow
This section provides the logic and flow required to calculate product prices as they will be displayed to shoppers in their country's local currency on the merchant's website.
The following flow is affected by the various rules, regulations, and specific price factors. Make sure to keep these in consideration when implementing the calculations. The field properties are detailed in Parameters, VAT Settings, and Applying Rounding Rules.
Product Price Calculation Logic and Flow
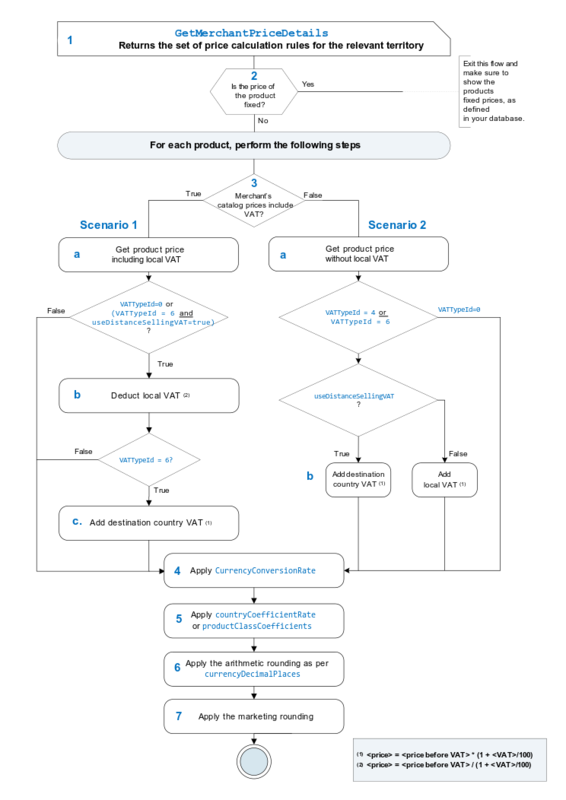
The following diagram provides the logic that enables the developer to calculate the international price of products based on parameters obtained when running the GetMerchantPriceDetails REST API.
 |
To implement the Product Price Logic and Flow:
Call the GetMerchantPriceDetails REST API to get the set of price calculation rules for the relevant territory.
Fixed prices: Check if at least some of the products have fixes prices.
If true, these products are configured as fixed prices in the merchant's database.
Fixed prices do not require additional calculation. Therefore, skip this entire flow. However, make sure to show the fixed prices for the products as set in your database.
For non-fixed prices, proceed as detailed below.
⇾
For each product, perform the following steps:
VAT settings: If you are a merchant from the European Union, proceed as follows. If you are a non-EU merchant, skip to step 4.
There are two VAT scenarios, depending on how you manage pricing in the e‑commerce platform.
Scenario 1
The price of the product in the merchant's system includes the local VAT.
Get the merchant's product price (including the local VAT).
Deduct the local VAT from the base price of the product if you selected one of the following VAT options:
VATTypeId = 0(hide/deduct the VAT)or
VATTypeID = 6anduseDistanceSellingVAT = true(This means that the product is shipped to a destination country where the distance selling regulation applies (within the EU))
Formula:
[price] = [price before VAT] / (1 + [VAT] / 100)
Add the destination country VAT to the base price of the product if:
VATTypeID = 6(force VAT).Formula:
[price] = [price without VAT] * (1 + [VAT]/ 100)
Otherwise, if the
VATTypeIDis not 0 or 6 and the rate of the destination country is not applicable,(useDistanceSellingVAT = False), proceed to step 4.
Scenario 2
The price of the product in the merchant's country does not include the local VAT.
Get the merchant's product price (without the local VAT).
Depending on the VAT options you choose, add the destination or local VAT to the base price of the product if the the product is shipped to a destination country where the distance selling regulation applies (within the EU):
if
VATTypeId = 0(hide/deduct the VAT), proceed to step 4.Add the destination VAT to the base price of the product if:
VATTypeID = 4(pocket VAT)or
VATTypeID = 6anduseDistanceSellingVAT = true(This means that the product is shipped to a destination country where the distance selling regulation applies (within the EU)).
Formula:
[price] = [price before VAT] * (1 + [destination VAT] / 100)
Add the local VAT to the base price of the product if:
VATTypeID = 4(pocket VAT)or
VATTypeID = 6anduseDistanceSellingVAT = false(This means that the product is shipped to a destination country where the distance selling regulation does not apply).
Formula:
[price] = [price before VAT] * (1 + [VAT] / 100)
See VAT Settings for field and option descriptions.
Apply the
currencyConversionRate.Apply the the
countryCoefficientRateor apply the correct rate from theproductClassCoefficientslist, according to the following:If the
countryCoefficientRateis not defined and theproductClassCoefficientis not defined, no coefficient is applied.If the
countryCoefficientRateis not defined and theproductClassCoefficientis defined, theproductCoefficientis applied.If the
countryCoefficientRateis defined and theproductClassCoefficientis not defined, thecountryCoefficientRateis applied.If the
countryCoefficientRateis defined and theproductClassCoefficientis defined, theproductClassCoefficientis applied.
Perform the arithmetic rounding:
Round up the currency's decimal places, leaving the same number of decimals defined in
currencyDecimalPlaces.Example:
If
currencyDecimalPlaces= 2And your currency = 223.0234512
Round up the number after the decimal =223.02
Calculate and apply the marketing rounding. See Applying Rounding Rules.
Basic rule for arithmetic rounding
If the number you are rounding is followed by a decimal and digits containing 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9, round the number up. Example: .29 rounded up to the nearest ten is .30
If the number you are rounding is followed by a decimal and digits containing 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4, round the number down. Example: .24 rounded down to the nearest ten is .20.
GetMerchantPriceDetails API
This API enables merchants to obtain the parameters required to calculate international product prices in a destination country's currency.
Example of Price Calculation Based on the VATTypeID
The following table is the list of VATTypeID values and descriptions and the expected results for a sample product with an original cost in UK = 100 GBP before VAT to be shipped to Germany (with a country coefficient Rate=1 and the user selected currency=GBP, for simplicity).
For this sample product UK VAT=20%, DE Duties Total=17%:
Include VAT Option Value | Description | Price in Browsing | Price in Checkout | Price Paid to Merchant (incl. VAT) | Checkout Duties Total | Checkout Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 | Hide VAT(default) | 100 | 100 | 120 | 17 | 117 |
4 | “Pocket” VAT (increase the original price by the value of the respective product’s VAT) | 120 | 120 | 144 | 20.4 (17%) | 140.4 |
6 | Force VAT (used to support trade agreements between the countries such as EEA, when end customer must pay VAT; for simplicity assuming UseCountryVAT=false) | 120 | 120 | 120 | 0 | 120 |
Applying Rounding Rules
After calculating the price of the product, you must apply the arithmetic and marketing rounding rules.
The arithmetic rounding rule is detailed in section Price Calculation Logic and Flow.
RangeBehaviors Enumeration
RangeBehavior Option Value | Name | Behavior Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Absolute target | All the values within the specified range (LowerTarget, UpperTarget, Threshold and RoundingExceptions) denote the values themselves as is, without the need for additional mathematical operations. To get rounding result (R) for the source number (S): If (S = Exceptionn) then R = Exceptionn If (S < Threshold) then R = LowerTarget If (S >= Threshold) then R = UpperTarget |
2 | Relative Decimal target | All the values within the specified range (LowerTarget, UpperTarget, Threshold and RoundingExceptions) represent floating point numbers between 0 (inclusive) and 1 (inclusive). To calculate the respective absolute values, relative to the calculation base (B):
If (S = EAn) then Result (R) = EAn If (S < TA) then R = LA If (S >= TA) then R = UA |
3 | Relative Whole target | All the values within the specified range (LowerTarget, UpperTarget, Threshold and RoundingExceptions) represent non-negative whole numbers. TargetBehaviorHelperValue (V) is used to determine the calculation base (B). V must be a power of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.) and denotes the order of magnitude for the range “split” by the Threshold. For example, if Threshold = 9, is this value is 9 out of 10 or 9 out of 100? To get rounding result (R) for the source number (S):
If (S = EAn) then Result (R) = EAn If (S < TA) then R = LA If (S >= TA) then R = UA |
4 | Nearest target | LowerTarget and UpperTarget represent non-negative floating point numbers. TargetBehaviorHelperValue (V) is used to determine the calculation base (B). V must be a whole divisor of any power of 10 (5, 10, 25, 50, 100, 250, 500, 1000, etc.). Threshold must be any floating point number between 0 (inclusive) and V (exclusive). To get rounding result (R) for the source number (S):
If (S = EAn) then Result (R) = EAn If (S < TA) then R = LA If (S >= TA) then R = UA |
Important
For any rounding behavior defined in the table above, if the rounding result is a negative number, it must be set to zero.
If either the LowerTarget or UpperTarget value violates the MaxDecimalPlaces setting for the respective currency, this value must be truncated.
For example, if UpperTarget is set to 0.999 for USD, it must be truncated to 0.99 before performing further calculations.
Rounding Rules Samples
The following samples indicate how rounding X to Y (X → Y) is implemented using the respective settings.
Property | 0.25 → 0 3 → 0 1.5 → 1.5 2 → 2 | 22.47 → 21.95 22.48 → 22.99 22.50 → 22.50 33.75 → 33.75 | 2047 → 1995 2048 → 2100 | 122.26 → 124.99 122.25 → 119.99 127.26 → 129.99 121.50 → 121.50 127.50 → 127.50 123 → 123 128 → 128 | 2047 → 1999 2048 → 2100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
From | 0 | 1 | 1000 | 100 | 1000 |
To | 3 | 250 | 10000 | 1000 | 10000 |
Threshold | 3.01 | 0.48 | 48 | 2.26 | 48 |
LowerTarget | 0 | 0.95 | 95 | 0.99 | 0 |
UpperTarget | 0 | 0.99 | 100 | 0.99 | 1 |
RangeBehavior | 1 Abolute | 2 Relative Decimal | 3 Reltive Whole | 4 Nearest | 4 Nearest |
TargetBehaviorHelperValue | 100 | 5 | 100 | ||
RoundingExceptions | 1.5 2 | 0.50 0.75 | 1.50 2.50 3 |
Price Conversion and Rounding Rule Implementation in JavaScript
This section shows an example of price conversion and rounding implementation in JavaScript. Use this example to write the APIs required for your specific environment and implement them.
function CalculatePrice(value, fxRate, vatRateTypes, productLocalVatRate, isGrossPrices, currencyDecimalPlaces, quantity, productClassCoefficient, priceCoefficient, productCountryVatRate, roundingRules) {
if (value == 0)
return (0).toFixed(currencyDecimalPlaces);
var merchantVatRate = vatRateTypes.LocalVATRateType.Rate / 100;
if (productLocalVatRate !== null) {
if (productLocalVatRate == 0) {
merchantVatRate = 0;
} else {
merchantVatRate = productLocalVatRate / 100;
}
}
var countryVatRate = vatRateTypes.VATRateType.Rate / 100;
if (productCountryVatRate || productCountryVatRate === 0) {
if (productCountryVatRate == 0) {
countryVatRate = 0;
} else {
countryVatRate = productCountryVatRate / 100;
}
}
if (isGrossPrices) {
if (vatRateTypes.IncludeVATTypeId == 0 ||
vatRateTypes.IncludeVATTypeId == 8 ||
(vatRateTypes.IncludeVATTypeId == 6 && vatRateTypes.UseCountryVAT)) {
value = value / (1 + merchantVatRate);
if (vatRateTypes.IncludeVATTypeId == 6) {
value += value * countryVatRate;
}
}
} else {
if (vatRateTypes.IncludeVATTypeId == 2 ||
vatRateTypes.IncludeVATTypeId == 4 ||
vatRateTypes.IncludeVATTypeId == 6) {
if (vatRateTypes.UseCountryVAT) {
value += value * countryVatRate;
} else {
value += value * merchantVatRate;
}
}
}
value = value * fxRate;
if (productClassCoefficient) {
value = value / priceCoefficient * productClassCoefficient;
}
value = value.toFixed(currencyDecimalPlaces);
if (skipRounding || roundingRules == null) {
value = value * quantity;
} else {
var ranges = roundingRules.RoundingRanges;
var range = null;
for (var r in ranges) {
var rg = ranges[r];
if (rg.From < value && value <= rg.To) {
range = rg;
break;
}
}
if (range != null) {
// convert range to form of absolute
range = ConvertRoundingRangeToAbsolute(value, range);
// apply logic of absolute range rounding
value = AbsoluteRounding(value, range) * quantity;
if (value < 0) {
value = 0;
}
}
}
return value;
};
function ConvertRoundingRangeToAbsolute(price, range) {
var result = null;
if (range.RangeBehavior == 1) {
// range already has absolute behavior
result = range;
} else {
result = new Object();
result.RangeBehavior = range.RangeBehavior;
result.RoundingExceptions = [];
result.From = range.From;
result.To = range.To;
var int_part = Math.floor(price);
if (range.RangeBehavior == 2) {
//Relative Decimal
result.LowerTarget = int_part - 1 + range.LowerTarget;
result.UpperTarget = int_part + range.UpperTarget;
result.Threshold = int_part + range.Threshold;
for (var ex in range.RoundingExceptions) {
range.RoundingExceptions[ex].ExceptionValue += int_part;
result.RoundingExceptions.push(range.RoundingExceptions[ex]);
}
} else if (range.RangeBehavior == 3) {
// Relative Whole
if (range.TargetBehaviorHelperValue == 0) {
range.TargetBehaviorHelperValue = 10;
}
var base = Math.floor(price /
range.TargetBehaviorHelperValue) * range.TargetBehaviorHelperValue;
result.LowerTarget = base - range.TargetBehaviorHelperValue + range.LowerTarget;
result.UpperTarget = base + range.UpperTarget;
result.Threshold = base + range.Threshold;
for (var ex in range.RoundingExceptions) {
range.RoundingExceptions[ex].ExceptionValue += base;
result.RoundingExceptions.push(range.RoundingExceptions[ex]);
}
} else if (range.RangeBehavior == 4) {
// Nearest target
if (range.TargetBehaviorHelperValue == 0) {
range.TargetBehaviorHelperValue = 5;
}
var base = Math.floor(price / range.TargetBehaviorHelperValue) * range.TargetBehaviorHelperValue;
result.LowerTarget = base - 1 + range.LowerTarget;
result.UpperTarget = base - 1 + range.TargetBehaviorHelperValue + range.UpperTarget;
result.Threshold = base + range.Threshold;
for (var ex in range.RoundingExceptions) {
range.RoundingExceptions[ex].ExceptionValue += base;
result.RoundingExceptions.push(range.RoundingExceptions[ex]);
}
}
}
return result;
};
function AbsoluteRounding(price, range) {
var result = null;
// check exceptions
if (range.RoundingExceptions.length > 0) {
for (var e in range.RoundingExceptions) {
ex = range.RoundingExceptions[e];
if (price == ex.ExceptionValue) {
result = price;
}
}
}
// no exception was found
if (!result) {
// check threshold
if (price < range.Threshold) {
result = range.LowerTarget;
} else {
result = range.UpperTarget;
}
}
return result;
};